As the second most populous country in the world and a rapidly growing economy, India plays a significant role in global trade. But what exactly is foreign trade policy in India? In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of India’s trade policies, exploring its history, objectives, and key features. Whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur looking to expand your business internationally or simply curious about how India engages with the global market, understanding its foreign trade policy is crucial. So buckle up and get ready for an enlightening journey into the world of Indian commerce.
Overview of foreign trade policy in India
India’s foreign trade policy plays a crucial role in promoting both domestic and international trade activities. With the aim of enhancing exports, reducing imports, and attracting foreign investment, the government has implemented various measures to facilitate trade. One such measure is the provision of incentives like Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) scheme that allows import of capital goods at concessional or zero duty rates for exporters. This policy not only encourages foreign investors but also supports local industries to upgrade their technology and increase production efficiency.
Furthermore, India’s foreign trade policy has laid emphasis on boosting export-oriented manufacturing through initiatives like Special Economic Zones (SEZs). These zones provide tax exemptions, simplified procedures, and world-class infrastructure to encourage companies to set up production units for exporting goods. Additionally, schemes such as Merchandise Export from India Scheme (MEIS) offer credits or benefits based on product-specific criteria encouraging exporters in different sectors. These initiatives demonstrate India’s commitment towards diversifying its export base by focusing on value-added products and emerging markets.
In recent years, with the growth of e-commerce platforms and digital technologies driving global trade, India’s foreign trade policy has also recognized the potential of online retailing as a significant avenue for exports. The introduction of policies like Know Your Customer guidelines for e-commerce platforms ensures transparency in cross-border transactions while enabling small businesses to participate actively in international trade. By embracing new opportunities offered by technology-driven commerce models, India aims to tap into global markets more efficiently while catering to evolving customer preferences.
History: Evolution of foreign trade policy
Throughout history, foreign trade policy has played a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of nations. In ancient times, the Silk Road was a vital trade route that connected Eastern and Western civilizations, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. This early form of globalization laid the foundation for future trade policies.
During the colonial era, European powers used their colonies as sources of raw materials and captive markets for their manufactured goods. The imposition of tariffs and trade restrictions served to maintain this favorable balance for the colonizers while hindering industrial development in their colonies.
In more recent times, countries have shifted towards liberalizing their trade policies. The establishment of institutions like the World Trade Organization (WTO) has led to increased cross-border flow of goods, services, and investments. One notable example is India’s shift from protectionist policies to a more open economy in the 1990s, which enabled it to tap into global markets and attract foreign investments.
These changes reflect an evolving understanding of how foreign trade can spur economic growth and development. While historically marred with exploitative practices and unequal power dynamics between nations, modern foreign trade policies aim to promote fair competition among countries while protecting domestic industries. By fostering international cooperation through agreements such as free-trade agreements or regional economic partnerships, governments seek to maximize opportunities for their businesses while addressing concerns related to labor rights, environmental sustainability, and intellectual property protection.
In conclusion, global commerce has undergone significant transformations over time. From ancient trading routes to colonization-driven mercantilism to today’s complex web of international trade, the nature and dynamics of global commerce have evolved. Advancements in technology, transportation, and communication have facilitated the growth of cross-border transactions and the integration of economies on a global scale.
Today, countries recognize that open markets can lead to economic growth and prosperity. However, they also acknowledge the need for regulations to ensure fair competition and protect domestic industries from unfair practices. This has led to the development of modern foreign trade policies that aim to strike a balance between promoting free trade and protecting national interests.
One of the key aspects of modern foreign trade policies is the establishment of bilateral and multilateral trade agreements. These agreements are negotiated between two or more countries and outline the terms and conditions under which trade will be conducted. They aim to reduce barriers to trade, such as tariffs and quotas, in order to promote economic integration.
Objectives: Goals and aims of the policy
The objectives, goals, and aims of a foreign trade policy in India are multifaceted and dynamic. One of the primary objectives is to enhance export competitiveness by providing various incentives and promoting market diversification. By focusing on reducing trade barriers and improving infrastructure, the policy aims to make Indian goods more competitive in the international market. Additionally, it also seeks to attract foreign investment and facilitate technology transfers to promote economic growth.
Another important goal of the foreign trade policy is to promote sustainable development through responsible trade practices. As India strives for inclusive growth, there is a strong emphasis on increasing employment opportunities, particularly in labor-intensive sectors like textiles and handicrafts. The policy aims to harness the potential of these sectors while ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions. Furthermore, environmentally friendly practices are encouraged through initiatives that support renewable energy production and waste management.
In concluding its objectives, it’s essential to highlight that the overarching aim of India’s foreign trade policy is to leverage globalization for socio-economic development while safeguarding national interests. With a focus on promoting small-scale industries and empowering women entrepreneurs, the policy seeks to create an inclusive business environment that spreads economic benefits across different sections of society. By aligning itself with global trends such as digitalization and e-commerce, this dynamic policy endeavors to position India as a major player in international trade while prioritizing social welfare concerns at its core.
Key features of current foreign trade policy
One of the key features of India’s current foreign trade policy is an increased focus on promoting exports and reducing trade barriers. The government has implemented several measures to facilitate ease of doing business for exporters, such as simplifying customs procedures, introducing online platforms for filing trade documents, and streamlining export incentives. This emphasis on boosting exports is crucial for India’s economic growth, as it helps in generating employment opportunities and enhancing the country’s competitiveness in the global market.
Another important feature of the foreign trade policy is the emphasis on diversification of both products and markets. India has traditionally been heavily reliant on a few sectors like textiles and pharmaceuticals for its exports, but there is growing recognition that diversification is essential to sustain long-term export growth. The government has introduced various schemes to encourage exporters to explore new sectors and markets through initiatives like Market Access Initiatives (MAI) scheme and Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS). These efforts not only help in reducing dependence on a few countries but also promote innovation and competitiveness among Indian exporters.
In addition to these features, India’s foreign trade policy also focuses on ensuring compliance with international regulations and increasing involvement in regional economic agreements. The government has taken steps to align domestic policies with international standards such as adopting WTO-compatible tariff rates, implementing stricter intellectual property rights protection laws, and actively participating in negotiations for regional free trade agreements like RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership). By actively engaging with other countries through these agreements, India aims to enhance market access for its exports and attract foreign investment.
To further promote its foreign trade, India has implemented various measures to streamline customs procedures and reduce trade barriers. The introduction of the Single Window Interface for Facilitating Trade (SWIFT) system has simplified the import/export clearance process by integrating multiple regulatory agencies onto a single platform. This not only expedites the movement of goods but also reduces administrative costs for traders.
Impact on Indian economy
The foreign trade policy in India has had a significant impact on the country’s economy over the years. One key aspect that cannot be ignored is the boost it has given to employment opportunities. With increased trade partnerships and liberalization of the Indian market, numerous jobs have been created, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, services, and agriculture. This has not only led to improved living standards for many Indians but also contributed towards reducing poverty levels in the country.
Another notable impact of the foreign trade policy is its effect on the manufacturing sector. As India became more integrated into the global economy, it attracted investments from multinational corporations looking to set up their manufacturing units in India. This influx of foreign investment brought with it advanced technologies and techniques that helped propel Indian industries forward. Additionally, by promoting exports and discouraging unnecessary imports, the foreign trade policy has played a crucial role in developing domestic industries and nurturing entrepreneurship within India.
Overall, it is clear that the foreign trade policy in India has had a profound impact on its economy. From job creation to technological advancements and growth of domestic industries, these policies have laid down a solid foundation for India’s economic development. It will be interesting to see how future policies further shape this dynamic landscape as India continues to strive for greater economic integration with other nations across the globe.
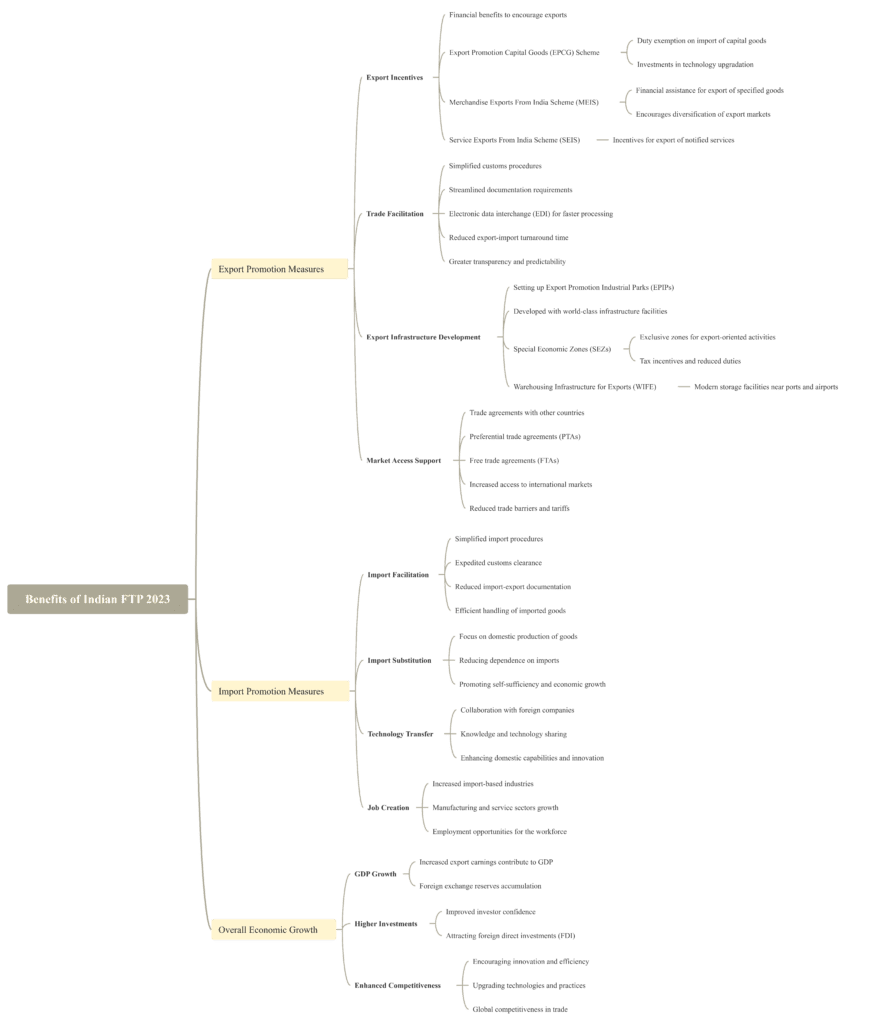
Components: Key elements of foreign trade policy
A key element of foreign trade policy is export promotion. With a focus on expanding India’s global presence, the government has implemented various measures to encourage exports. This includes providing incentives and benefits such as duty drawback schemes, export subsidies, and tax refunds. By promoting exports, the aim is to boost economic growth, create employment opportunities, and enhance India’s competitiveness in the international market.
Import regulation is another crucial component of foreign trade policy. The government takes measures to regulate imports by imposing barriers such as tariffs and import quotas. These regulations are put in place to protect domestic industries from unfair competition and prevent dumping of goods at below-market prices. Additionally, import restrictions may also be implemented for strategic or security reasons. However, it is important for policymakers to strike a balance between protecting domestic industries and promoting international trade for overall economic growth.
Foreign investment policies play a significant role in shaping foreign trade policy as well. The Indian government has liberalized its foreign direct investment (FDI) regime over the years to attract capital inflows and promote technology transfer through joint ventures with foreign companies. FDI policies often dictate how much stake a foreign investor can hold in an Indian company, the sectors open for investment, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. A favorable FDI policy framework encourages investments from abroad while ensuring that national interests are safeguarded.
By carefully considering these components – export promotion, import regulation, and foreign investment policies – India’s foreign trade policy strives to strike a balance between protecting domestic industries and promoting economic growth and global integration.
To protect domestic industries, India’s foreign trade policy includes measures such as import regulations. These regulations aim to restrict the entry of certain goods that can be produced domestically, thereby safeguarding local manufacturers from unfair competition. The government may impose tariffs or quotas on specific products to control their import quantities and maintain a level playing field for domestic producers.
At the same time, India recognizes the importance of global integration and actively promotes exports. Export promotion schemes are implemented to provide incentives and support.
Initiatives: Recent initiatives and reforms in the policy
One of the recent initiatives in India’s foreign trade policy is the introduction of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, also known as the Self-Reliant India Mission. This initiative aims to promote domestic manufacturing and reduce reliance on imports by boosting local production and enhancing export competitiveness. The government has announced various measures under this mission, such as providing financial assistance to key sectors, incentivizing domestic manufacturers, simplifying regulations, and promoting research and development.
Another significant reform in the policy is the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST). The GST aims to streamline taxation across different states and create a unified market for goods and services. By eliminating multiple tax barriers and reducing compliance costs, this reform has made it easier for businesses to engage in cross-border trade. The introduction of GST has not only improved transparency but also enhanced efficiency in supply chains, thus encouraging international trade activities.
These recent initiatives reflect India’s commitment to revamping its foreign trade policy for sustainable economic growth. By prioritizing domestic production capabilities through initiatives like Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, India aims to become self-reliant while simultaneously boosting exports. Moreover, reforms such as GST have improved ease of doing business in India, attracting more foreign investment and expanding opportunities for international trade partnerships. These initiatives are crucial steps towards ensuring a stronger position in the global market for Indian businesses while driving overall economic development.
Challenges: Issues and obstacles faced in implementation
Implementing foreign trade policy in India is not without its fair share of challenges. One of the major obstacles faced in implementation is the complex web of regulations and procedures. The bureaucratic red tape often leads to delays and confusion, making it difficult for businesses to navigate through the various documentation requirements and licensing processes.
Another significant challenge lies in ensuring compliance with international standards and trade agreements. India has signed a number of free trade agreements (FTAs) and is a member of various regional trading blocs. However, complying with these agreements can be daunting for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) who may lack the necessary resources or information to adapt their production processes or meet quality standards stipulated by importing countries.
Moreover, infrastructure deficits pose a considerable challenge in implementing foreign trade policies. Inadequate transportation systems, outdated port facilities, and cumbersome customs procedures can hinder efficient movement of goods across borders. This not only increases transaction costs but also negatively impacts India’s competitiveness in global markets.
Overall, while India’s foreign trade policy aims to promote exports, attract investment, and integrate into global value chains, several issues need to be addressed for effective implementation. Simplifying regulations, providing capacity-building support to SMEs, improving infrastructure, and enhancing coordination among government agencies are key steps that can help overcome these challenges.
Conclusion: Importance and future prospects of the policy
In conclusion, the foreign trade policy in India plays a crucial role in shaping the country’s economic growth and development. It has helped India become a major player in international trade and attract foreign direct investment. The policy has been instrumental in promoting exports, improving competitiveness, and diversifying the export base.
Looking towards the future, the importance of the foreign trade policy cannot be overstated. The dynamic global economy calls for constant adaptation and innovation to stay competitive. With rapid advancements in technology and changing global trade patterns, it is imperative that India continues to review and update its policies to seize new opportunities arising from emerging markets.
Moreover, as India aims to become self-reliant through initiatives like Make in India, there will be a need for further reforms that enhance ease of doing business and reduce bureaucratic hurdles. Encouraging domestic manufacturing along with boosting exports will require strategic planning and targeted interventions through an effective foreign trade policy.
Overall, it is clear that the success of Indian businesses in international markets relies heavily on a well-thought-out foreign trade policy. By providing a stable framework for conducting business, it paves the way for increased investments, job creation, improved productivity, and ultimately achieving higher economic growth for the nation. As we move forward into an increasingly interconnected world economy, continuing efforts to strengthen this policy will be vital for securing India’s position as a global trading hub.
